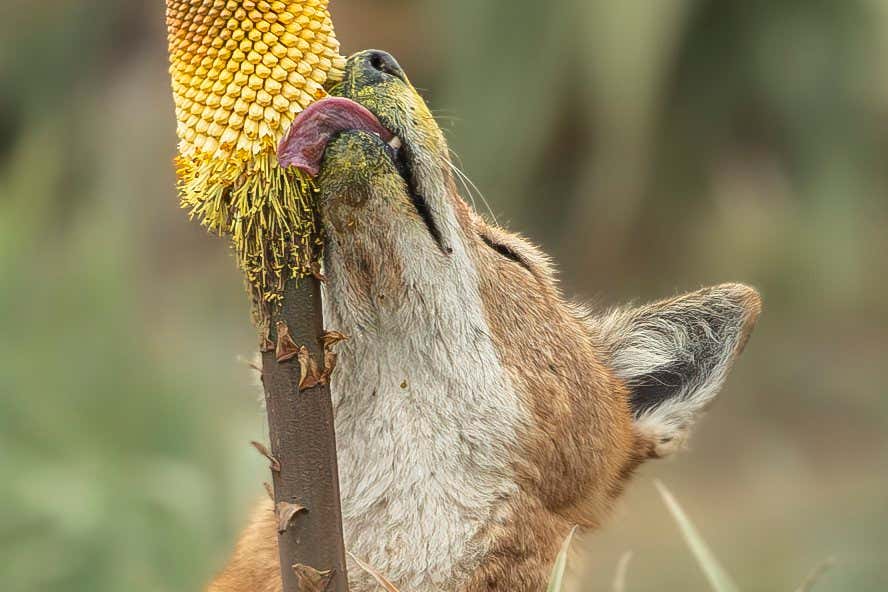
An Ethiopian wolf licks nectar from the Ethiopian red hot poker flower
Adrien Lesaffre
Ethiopian wolves feed on the sweet nectar of a local flower, picking up pollen on their snouts as they do so – which may make them the first carnivores discovered to act as pollinators.
The Ethiopian wolf (Canis simensis) is the rarest wild canid species in the world and Africa’s most threatened carnivore. Endemic to the Ethiopian Highlands, fewer than 500 individuals survive.
Advertisement
Sandra Lai at the University of Oxford and her colleagues observed wild Ethiopian wolves lapping up the nectar of Ethiopian red hot poker (Kniphofia foliosa) flowers. Local people in the mountains have traditionally used the nectar as a sweetener for coffee and on flat bread.
The wolves are thought to be the first large carnivore species ever to be recorded regularly feeding on nectar.
“For large carnivores, such as wolves, nectar-feeding is very unusual, due to the lack of physical adaptations, such as a long tongue or specialised snout, and because most flowers are too fragile or produce too little nectar to be interesting for large animals,” says Lai.
The sturdy, nectar-rich flower heads of the poker plant make this behaviour possible, she says. “To my knowledge, no other large carnivorous predator exhibits nectar-feeding, though some omnivorous bears may opportunistically forage for nectar, albeit rarely and poorly documented.”
Some of the wolves were seen visiting as many as 30 blooms in a single trip. As they lick the nectar, the wolves’ muzzles get covered in pollen, which they could potentially be transferring from flower to flower as they feed.
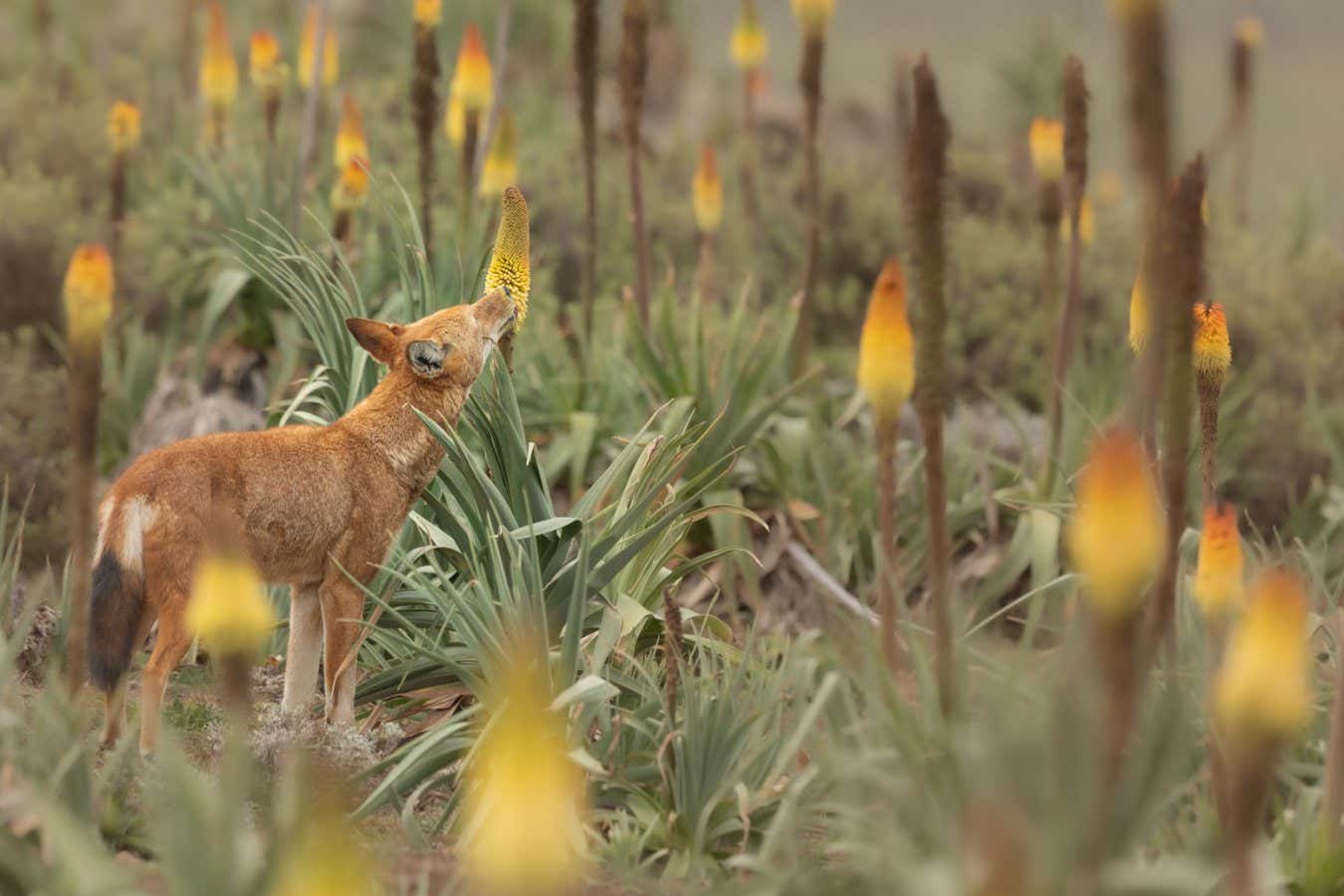

Nectar feeding is very unusual among carnivores
Adrien Lesaffre
“The behaviour is interesting because it shows nectar-feeding and pollination by non-flying mammals might be more widespread than currently recognised, and that the ecological significance of these lesser-known pollinators might be more important than we think,” says Lai. “It’s very exciting.”
Lai and her colleagues at the Ethiopian Wolf Conservation Programme now hope to dig deeper into the behaviour and its ramifications. “Trying to confirm actual pollination by the wolves would be ideal, but that would be quite challenging,” she says. “I’m also very interested in the social learning aspect of the behaviour. We’ve seen this year adults bringing their juveniles to the flower fields, which could indicate cultural transmission.”
Topics: